Sources and Structure of Diindolylmethane (DIM)
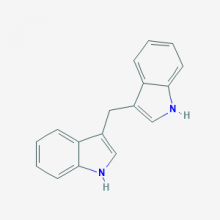
Structure of Diindolylmethane (DIM)
Diindolylmethane (DIM) is the primary pharmaceutically active acid-derived metabolic of Indole-3-Carbinol (I3C) which is found in many Brassica vegetables via the mother compound glucobrassicin. Ingested glucobrassicin is catalyzed via the enzyme Myrosinase (stored in vegetables) and turns into Indole-3-Carbinol, which is quickly digested into both DARKISH and several other metabolites in the human stomach via acid-mediated condensation reactions.
where 3 3'-diindolylmethane (dim) comes from
Options for Glucosinolates (in general) are detailed below:
- Brussel Sprouts, at 104mg for each 44g (half cup)
- Back garden Cress, 98mg at 25g (half cup)
- Mustard Greens, 79mg at 28g (half cup, chopped)
- Turnip, 60mg at 65g (half cup, cubes)
- Savoy Cabbage, 35mg at 45g (half glass, chopped)
- Kale, 67mg each 67g (1 cup, chopped)
- Watercress, 32mg per 34g (1 cup, chopped)
- Kohlrabi, 31mg per 67g (half cup, chopped)
- Red Cabbage, 29mg per 45g (half cup, chopped)
- Broccoli, 27mg each 44g (half cup, chopped)
- Horseradish, 24mg per 15g (tablespoon)
- Cauliflower, 22mg per 50g (half-cup chopped)
- Bok Choy, 19mg per 35g (half cup, chopped)
Glucosinolates and 3 3'-diindolylmethane
Glucobrassicin is a type of glucosinolate that can be found in almost all cruciferous plants, such as cabbages, broccoli, mustards, and woad. As for other glucosinolates, degradation by the enzyme myrosinase is expected to produce an isothiocyanate, indol-3-ylmethylisothiocyanate. However, this specific isothiocyanate is expected to be highly unstable, and has indeed never been detected. The observed hydrolysis products when isolated glucobrassicin is degraded by myrosinase are indole-3-carbinol and thiocyanate ion (plus glucose, sulfate, and hydrogen ion), which are envisioned to result from a rapid reaction of the unstable isothiocyanate with water. However, a large number of other reaction products are known, and indole-3-carbinol is not the dominant degradation product when glucosinolate degradation takes place in crushed plant tissue or in intact plants.
As glucobrassicin degrades into I3C by the plant-contained enzyme Myrosinase, deactivation with this enzyme by heat-treatment is able to reduce the oral bioavailability of any glucosinolate including POOR. Some bioavailability is stored, yet, due to individual intestines expressing Myrosinase as well.
Cooking food and ] seem to be most suspect in minimizing glucosinolate bioavailability; the past due to excess normal water sapping water-soluble bio actives from the food. Along these lines, cooking methods that utilize less water keep more glucosinolates than do those using lots of water.
Glucosinolates will surely have their absorption rates reduced by cooking, and low-temperature piping-hot may be the most efficient way to protect glucosinolate content of veggies.
Send inquiry online For more product information and prices
(Pharmaceutical Ingredients Manufacturer & Supplier & Exporter.)
After sending the online inquiry, we will reply you as soon as possible, if not get any response on time please contact us by Tel or Email. —— Green Stone Swiss
Email: sales@raw-pharmaceutical-materials.comTel: +86 592 5365887
WhatsApp: +86 189 6515 7632
Send inquiry online:

