FDA approves Aemcolo ( rifamycin )
November 16, 2018, The U.S. Food and Drug Administration today approved Aemcolo (rifamycin), an antibacterial drug indicated for the treatment of adult patients with travelers’ diarrhea caused by noninvasive strains of Escherichia coli (E. coli), not complicated by fever or blood in the stool.
"Travelers' diarrhea affects millions of people each year and having treatment options for this condition can help reduce symptoms of the condition," said Edward Cox, M.D., M.P.H., director of the Office of Antimicrobial Products in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research.
Travelers' diarrhea is the most common travel-related illness, affecting an estimated 10 to 40 percent of travelers worldwide each year. Travelers' diarrhea is defined by having three or more unformed stools in 24 hours, in a person who is traveling. It is caused by a variety of pathogens, but most commonly bacteria found in food and water. The highest-risk destinations are in most of Asia as well as the Middle East, Africa, Mexico, and Central and South America.
The efficacy of Aemcolo was demonstrated in a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial in 264 adults with travelers’ diarrhea in Guatemala and Mexico. It showed that Aemcolo significantly reduced symptoms of travelers’ diarrhea compared to the placebo.
The safety of Aemcolo, taken orally over three or four days, was evaluated in 619 adults with travelers’ diarrhea in two controlled clinical trials. The most common adverse reactions with Aemcolo were headache and constipation.
Aemcolo was not shown to be effective in patients with diarrhea complicated by fever and/or bloody stool or diarrhea due to pathogens other than noninvasive strains of E. coli and is not recommended for use in such patients. Aemcolo should not be used in patients with a known hypersensitivity to rifamycin, any of the other rifamycin class antimicrobial agents (e.g. rifaximin), or any of the components in Aemcolo.
The FDA granted Aemcolo a Qualified Infectious Disease Product (QIDP) designation. QIDP designation is given to antibacterial and antifungal drug products that treat serious or life-threatening infections under the Generating Antibiotic Incentives Now (GAIN) title of the FDA Safety and Innovation Act. As part of QIDP designation, the Aemcolo marketing application was granted Priority Review under which the FDA’s goal is to take action on an application within an expedited time frame.

| Name: | Rifamycin |
|---|---|
| CAS No.: | 15105-92-7 |
| Formula: | C37H47NO12 |
| Chemical Names: | Rifamycin SV; RIFAMYCIN; Rifamicina; Rifamycine; Rifamycinum; Rifocin |
| Molecular Weight: | 811.926 g/mol |
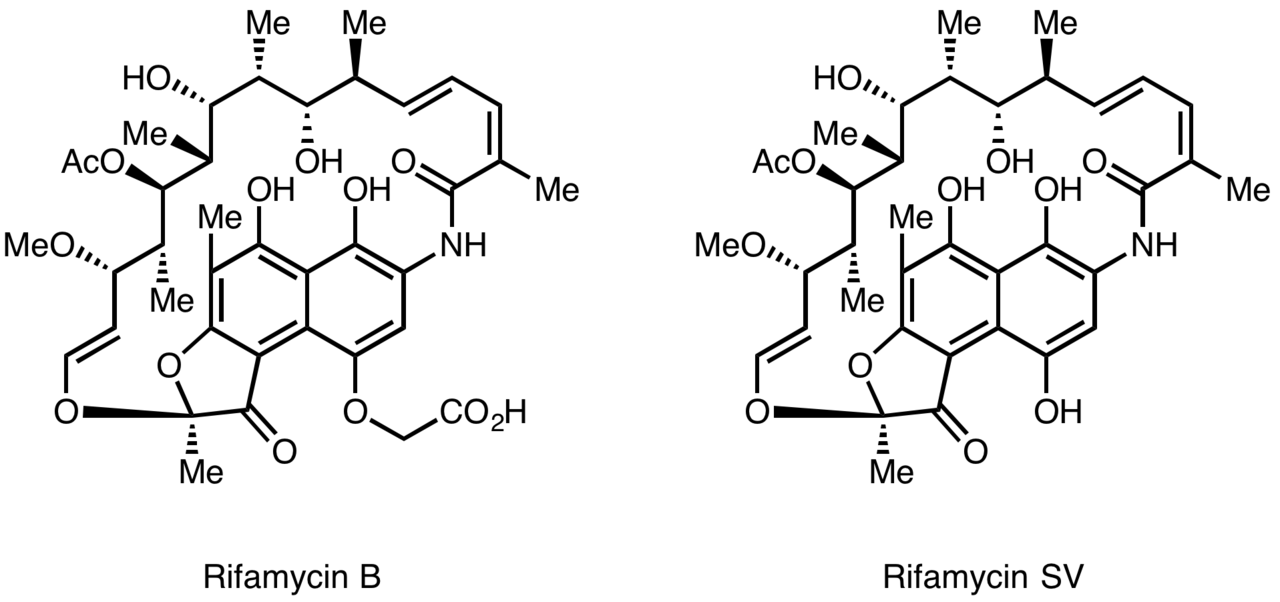
Rifamycins were first isolated in 1957 from a fermentation culture of Streptomyces mediterranei at the laboratory of Gruppo Lepetit SpA in Milan by two scientist named Piero Sensi and Maria Teresa Timbal, working with the Israeli scientist Pinhas Margalith. Initially, a family of closely related antibiotics was discovered referred to as Rifamycin A, B, C, D, E. The only component of this mixture sufficiently stable to isolate in a pure form was Rifamycin B, which unfortunately was poorly active. However, further studies showed that while Rifamycin B was essentially inactive, it was spontaneously oxidized and hydrolyzed in aqueous solutions to yield the highly active Rifamycin S. Simple reduction of Rifamycin S yielded the hydroquinone form called Rifamycin SV, which became the first member of this class to enter clinical use as an intravenous antibiotic. Further chemical modification of Rifamycin SV yielded an improved analog Rifamide, which was also introduced into clinical practice, but was similarly limited to intravenous use. After an extensive modification program, Rifampin was eventually produced, which is orally available and has become a mainstay of Tuberculosis therapy.
DRUG TRIALS SNAPSHOT SUMMARY:
What is the drug for?
AEMCOLO is a drug for the treatment of adult patients with travelers’ diarrhea which is
- caused by noninvasive type of Escherichia coli, and
- not complicated by fever or blood in the stool.
Travelers' diarrhea is a condition defined by having three or more unformed stools in 24 hours, in a person who is traveling.
How is this drug used?
Two tablets of AEMCOLO are taken by mouth twice daily for three days.
What are the benefits of this drug?
In the trial, patients who took AEMCOLO experienced shorter duration of diarrhea (by approximately 22 hours) in comparison to patients who took placebo.
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race and age?
- Sex: AEMCOLO worked similarly in men and women.
- Race: The majority of patients in the trials were White. Differences in how well AEMCOLO worked among races could not be determined.
- Age: The majority of patients in the trials were younger than 65 years of age. Differences in how well AEMCOLO worked in patients younger and older than 65 years of age could not be determined.
The FDA granted approval of Aemcolo to Cosmo Technologies, Ltd.
URL: https://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm626121.htm
URL: https://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ucm626831.htm
URL: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/6438465
URL: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rifamycin
Send inquiry online For more product information and prices
(Pharmaceutical Ingredients Manufacturer & Supplier & Exporter.)
After sending the online inquiry, we will reply you as soon as possible, if not get any response on time please contact us by Tel or Email. —— Green Stone Swiss
Email: sales@raw-pharmaceutical-materials.comTel: +86 592 5365887
WhatsApp: +86 189 6515 7632
Send inquiry online:

